

You can see the code for all the deletion below 4.3.
To delete the last element from the doubly linked list, traverse till the second last element (using current.next != null and keeping track of the previous node) and change the previous node’s next to null.You can see the illustration in the following diagram.
Also, current node’s next’s previous has to point to previous node.You can see the illustration in the following diagram.

We then traverse till the index (using the current.next != null and by keeping track of current and previous node) and change the previous node’s next to the current node’s next. To delete an element at the index from the doubly linked list, we first check if the index is less than the size of the list. You can see the illustration in the following diagram. To delete the first node from the doubly linked list, point the head to the current first nodes next. To delete a node from the doubly linked list, we need to do the following steps. Like insertion, we can delete a node from a doubly linked list in 3 ways.
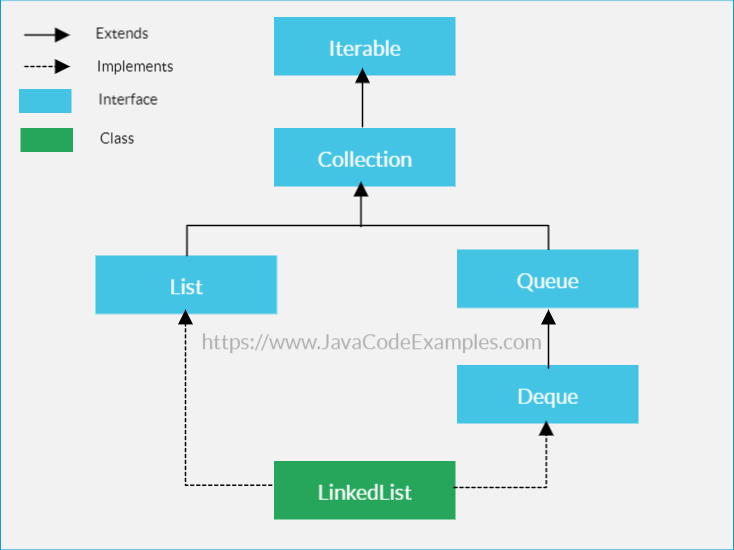
The new node’s next will point to NULL now.Īs you can see below, we had a linked list 123NULL and we want to insert node 4 at last, so we will change the pointers as per the above steps and the linked list will become 1234NULL. The new node’s previous will point to the current node. The current last node’s next will point to the new node. At this stage we will do the following 3 things: When we want to insert a node at the end of a doubly linked list, we will traverse the doubly linked list till the current’s next points to NULL. The current node’s previous will point to the new node.Īs you can see below, we had a linked list 134 and we want to insert node 2 at index 1, so we will change the pointers as per the above steps and the linked list will become 1234. The new node’s previous will point to current’s previous. The current node’s previous’s next will point to the new node. The new node’s next will point to the current node. If we wish to insert a node at any index, we will first check if the index is less than the size of the list, we will then first traverse till the index. As you can see below, we had a linked list 123 with the head pointing to 1 and we added a new node 0 and the linked list becomes 0123 with the head pointing to node 0 now. The head will now point to the newly added node. I will add the new node before the first node of the doubly linked list and its next will point to previous first node. In a doubly linked list, we can insert a node in three different ways. We will go through the major operations of a linked list, and they are insertion, deletion, display, search, and size. The first node’s previous pointer points to NULL. The last node’s next pointer points to NULL. Each node has a data field, a pointer to previous node and a pointer to the next node. The Head node points to the first node of the list. Each node contains a value (data), a pointer to the next node, and a pointer to the previous node in the sequence.Īs per the above illustration, the following are the important points to be considered. Doubly Linked List RepresentationĪ doubly linked list is made of a sequence of nodes. We need to maintain both the next and previous pointer while inserting a new node. Insertion or deletion operations require an extra pointer (previous) to be maintained. Typical disadvantage is that a doubly linked list node requires extra space for storing the previous pointer. Deleting a node is also easy as we need not traverse the entire list to find the previous node as with the singly linked list. Adding a new node is just about changing the pointers. Major advantage of a doubly linked list is that we can traverse it in both directions. The two pointers help to traverse both in forward and backward direction though it takes extra space for storing the previous pointer. The previous pointer of the first node of the list points to NULL and the next pointer of the last node also points to NULL. The previous pointer points to the previous node in the list and the next pointers points to the next node in the list. Along with these two pointers, it also contains the data. Advertisements What is a Doubly linked list in JavaĪ Doubly Linked List (DLL) contains two pointers instead of one in Singly Linked List, we call them previous and next.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
